GENERAL INFORMATION:
Oligonucleotides are short DNA chains which are made up from, Adenine, Guanine Cytosine and Thymine, the DNA basses. Molecular biologists often use oligonucleotides (also called “oligo” or “primer” for short) in many branches of their profession. Oligos are not only used for; detection of certain organisms, mutations and basses in a DNA, but also, to create and amplify DNA (through PCR amplification), creating desired mutations (through mutagenesis) and general genetic manipulation. Furthermore some of these methods are used in medical fields in order to predict genetic traits that may cause certain illnesses and to confirm clinical findings. Every oligonucleotide is chemically synthesized from the special designs, tailored according to the expected use.
According to its purpose, oligonucleotides can be further specialized by attaching different molecules in the ends of the chain or between the basses. By using some of these molecules can have fluorescence properties thus emitting light in pre-designed wavelengths, while through use of other molecules the oligo can attach to solid surfaces or an another molecule. These modifications, in some cases can be attached during the synthesis phase, while some can be attached afterwards.
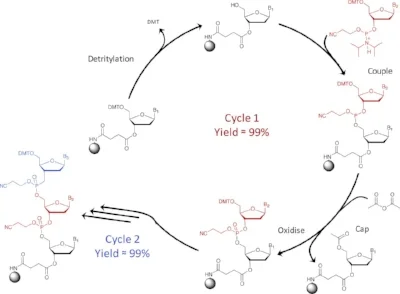
Phosphoramidite chemistry (also called “solid phase synthesis”) is the most established method in oligonucleotide synthesis. In this method each oligo begins with a CPG column (controlled pore glasses). These columns are made from silica particles with a diameter of 1000 Angstroms which act as the solid support for the oligo to be built. Due to this, CPG type determines the scale of the synthesis.
There is a common misconception that synthesis scale equals to the yield of the scale. Due to the chemical nature of this process yield of the synthesis is not 100% due to coupling efficiency. The yield of an oligonucleotıde is inversely proportional to the length of the oligo thus as the length of the oligo nucleotide increases the less yield will be achieved. Moreover, it is unavoidable to lose some of this yield during the purification process. A safe assumption to have while ordering an oligo nucleotide is to expect the final yield to be around 50% of the synthesis scale.
As mentioned, during the phosphoramidite cycle, due to coupling efficiency, that overall yield is less than the synthesis scale. This difference is usually expressed in the synthesis as “short-oligos” . These structures are impurities for the final oligo therefore must be purified. There 3 types of purification methods that are available; standard desalting, RPC (Reverse Phase Cartridge) and HPLC (Hıgh Performance Liquid Chromatography). If removal of these impurities is at high importance, it is advised to use RPC or HPLC method. Choose the method most suited to your needs.